The EFQM Excellence Model: Capturing Quality & Business Improvement
Victoria GlancyWhat makes organisations excellent? This is the question posed and answered by the EFQM Excellence Model which is the European standard for Quality. The point of quality is sustained and continuous improvement over time benefiting both the organisation and the customer which is why organisations have increasingly looked to implement quality focused initiatives such as the EFQM Model.
But what is the EFQM Model and why is it a necessary focus of business improvement?
The Origins of the EFQM Model
This model was introduced in 1992, partly due to the vulnerability felt by the countries of Europe towards Japan, who at the time were leaps and bounds ahead in respect of Quality. The Toyota Way is often still quoted as best practice for manufacturing companies.
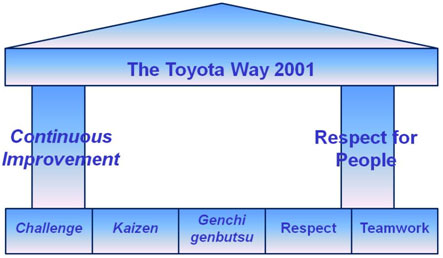
Image from http://riboparts.com/
If you're looking to implement a quality and Business Improvement culture in your organisation but don't know where to start then please take our simple 6 question  which will help us to identify your unique issues and find a solution that best suits your needs.
which will help us to identify your unique issues and find a solution that best suits your needs.
What is so Excellent About the EFQM Excellence Model?
The EFQM’s definition of excellent organisations are those that:
'Achieve and sustain outstanding levels of performance that meet or exceed the expectations of all their stakeholders'
To achieve ‘sustained’ levels of performance organisations have to support a continuous improvement programme to ensure they remain excellent. Much like the Toyota Way
It is also interesting to note that the definition highlights ‘stakeholders’. There can be a variety of stakeholders for any business or organisation and to be classed as excellent they have to be achieving an outstanding level of performance for all of their different stakeholders; employees, customers, shareholders, owners, the wider community.
The EFQM Excellence model allows people to understand the cause and effect relationships between what their organisation does, the Enablers, and the Results it achieves.
The model comprises three integrated components:
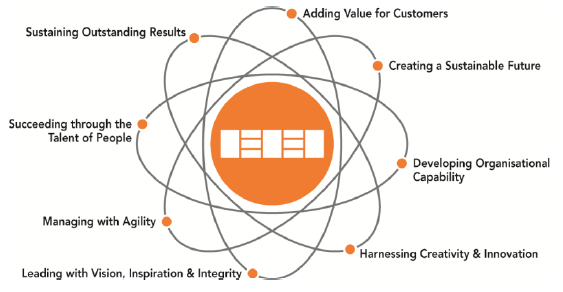
The Fundamental Concepts of Excellence
The Fundamental Concepts define the 8 underlying principles that form the foundation for achieving sustainable excellence in any organisation:
- Adding value for customers
- Creating a sustainable future
- Harnessing creativity and innovation
- Managing with agility
- Developing organisational capability
- Leading with vision, inspiration and integrity
- Succeeding through the talent of people
- Sustaining outstanding results
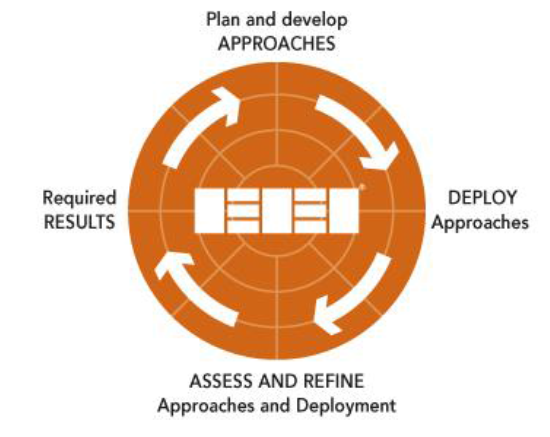
The RADAR
At the highest level RADAR logic states that an organisation should:
- Determine the Results it is aiming to achieve as part of its strategy.
- Plan and develop an integrated set of sound Approaches to deliver the required results both now and in the future.
- Deploy the approaches in a systematic way to ensure implementation.
- Assess and Refine the deployed approaches based on monitoring and analysis of the results achieved and on-going learning activities.
The Criteria
The Criteria provide a framework to help organisations to convert the Fundamental Concepts and RADAR thinking into practice.
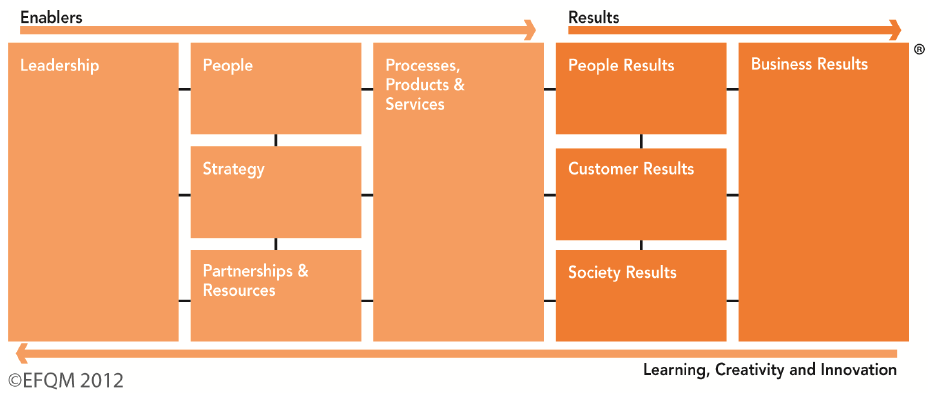
As can be seen from the image above, there are 5 enablers.
- Leadership
- People
- Strategy
- Partnership and resources
- Processes, products and services
These are the things that an organisation need to do to develop and implement their strategy.
Process Capture, Management & Improvement
Organisations frequently use the Triaster platform to support them with the process capture, management and improvement of their processes, so we will only focus here on the enabler Processes, Products & Services. The EFQM state that:
'Excellent organisations design, manage and improve processes to generate increasing value for customers and other stakeholders.'
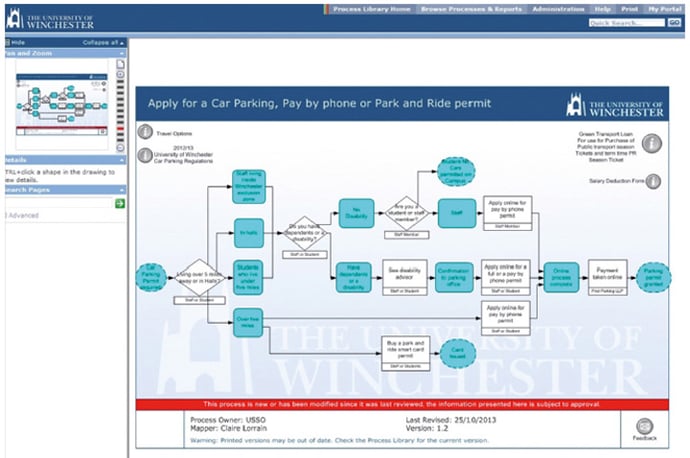
Gaining a better understanding of their business processes, always enables organisations to better understand what it is they are delivering, prioritise areas of improvement and establish a baseline for continual improvement.
Organisations striving to implement the EFQM Excellence Model are required to showcase that all their key business processes are regularly and systematically reviewed and refined and that process capture/improvement skills and techniques are widely used throughout the organisation.
The EFQM Model gives many organisations the push they need to create a culture of quality and continual improvement throughout the organisation. Read our  for more practical information displaying how 8 organisations took their business problems and turned them into sustained and continuous business improvement using process capture and process management.
for more practical information displaying how 8 organisations took their business problems and turned them into sustained and continuous business improvement using process capture and process management.
Related articles:
Capturing Waste in a process: Value-stream and the 7 wastes
How to create a Process Map in 3 simple steps
What is the Noun-verb methodology of Process Mapping?
Note:
This is an updated and refreshed version of an article originally written by Victoria Glancy.
Written by Victoria Glancy
In August 2017, Triaster’s Client Service Director Victoria Glancy moved on to become the Managing Director of Libreea Ltd. With a background in analytical science, Victoria has honed her analysis and requirement capture skills from working across several industries with the public and private sectors and is very proud of the achievements and progression she made whilst at Triaster. Initially working as Triaster's Customer Project Support Consultant, she learnt 'at the coalface' what is important to a project team implementing Business Process Management and Improvement. From here Victoria became a very successful Client Services Director. With her ability to quickly gain a clear understanding of customers' requirements and how they can best be achieved she was able to successfully support a varied selection of both new and existing customers. As the Managing Director of Triaster’s sister company Libreea, Victoria is now building on her experiences further and developing this ability by providing a set of bespoke Business Management Services tailored to your unique business challenges.
